The background of Motion Detection
Basics of Motion Detection
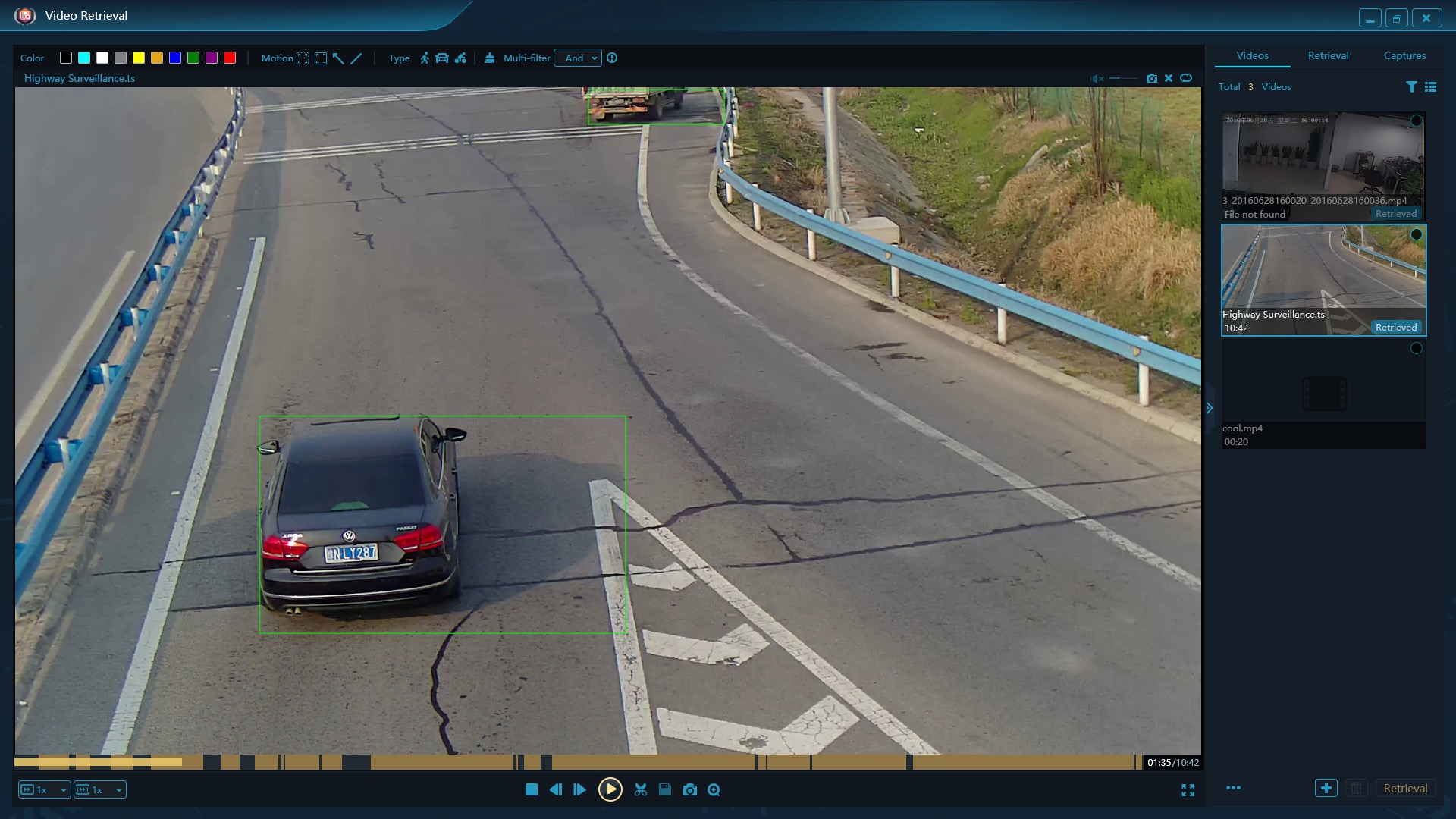
At its core, motion detection is a process of analyzing video frames to detect changes in pixel values. When a pixel changes significantly from one frame to the next, it may indicate the presence of movement in the scene.
There are many different algorithms and techniques that can be used to perform motion detection, and VIP 2.0’s algorithm is highly customizable.
This means that investigators can adjust the sensitivity of the algorithm to detect different types of motion, such as large movements or subtle changes in lighting.
Anatomy of Motion Detection
Theoretically, Motion detection is an essential component of modern video forensics, allowing investigators to quickly identify potentially relevant events in a scene.
The theory behind motion detection is relatively straightforward: when an object moves across a video frame, it creates changes in pixel values that can be detected and analyzed.
3 common algorithms in motion detection
According to “Video Forensics: From Live Acquisition to Analysis,” edited by Chaminda Hewage and David A. Stirling, there are several different algorithms that can be used to detect motion in a video, including background subtraction, optical flow, and frame differencing.
Each of these algorithms works by comparing the current frame of the video to a reference frame or background image and then analyzing the differences between the two.
- Background subtraction is one of the most common motion detection algorithms and involves creating a background model of a video scene by averaging pixel values over time. Then, as new frames of the video are acquired, the background model is subtracted from the current frame to identify areas where there is a significant difference. These areas are flagged as potential motion events.
- Optical flow, on the other hand, tracks the movement of individual pixels across consecutive frames of a video. By calculating the speed and direction of pixel movement, this algorithm can detect and track the motion of objects in the scene. This technique is particularly useful for detecting motion in scenes with complex backgrounds, where background subtraction may not be effective.
- Frame differencing is another common motion detection algorithm that compares the differences between consecutive frames of a video. Pixels that have a significant difference in value are flagged as potentially relevant motion events. This technique is useful for detecting sudden changes in a scene, such as the entry of a person or vehicle.