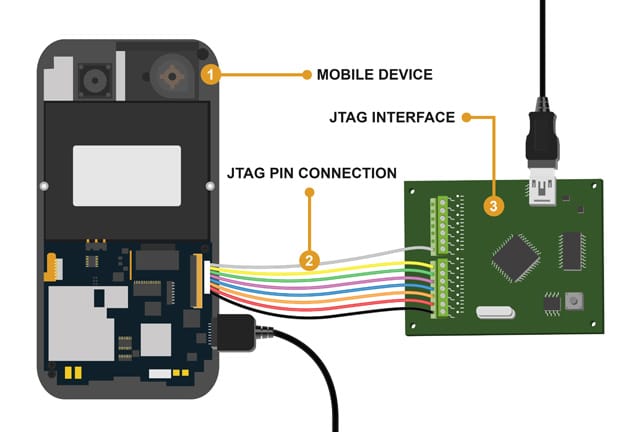
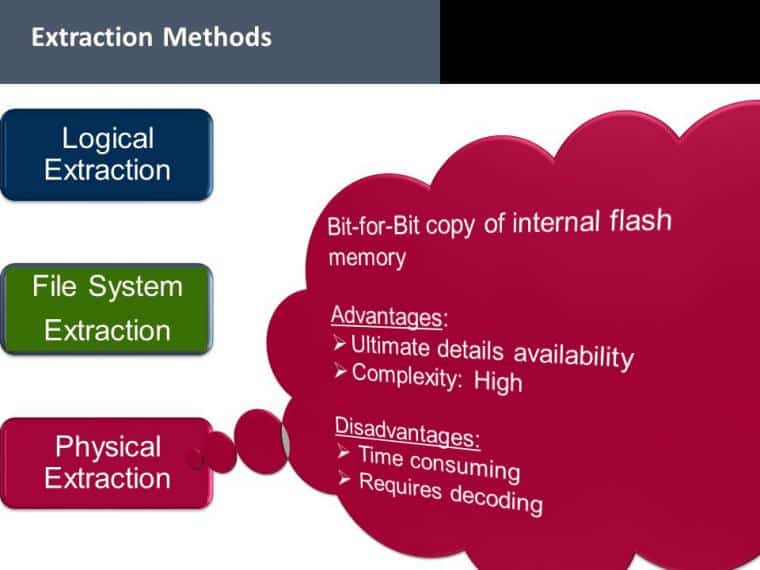
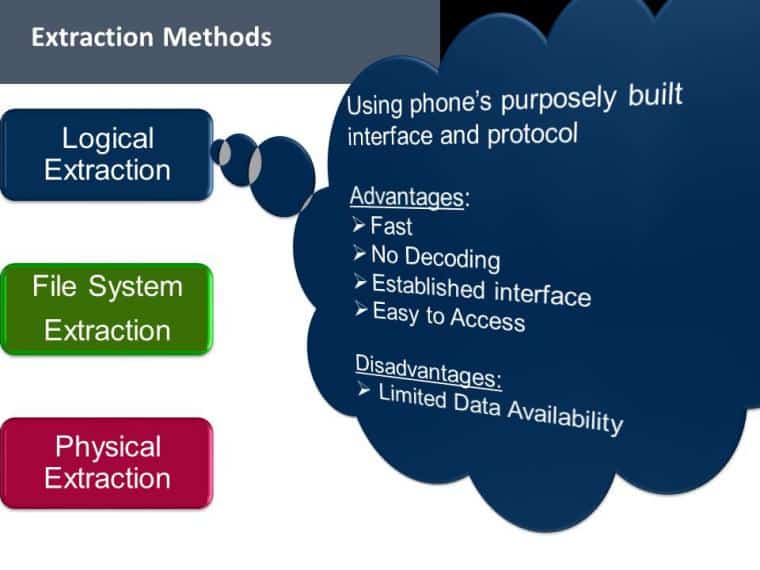
Within the field of digital forensics, the capacity to retrieve data from cellphones that have been locked is a crucial skill that determines the success of an inquiry. Since smartphones may frequently be the key to solving complicated cases, smartphone forensics has emerged as a critical component in the war on crime and terrorism. Phone records, text messages, emails, and even location data may all be found on locked devices, and these details can be quite valuable in gaining insight into criminal activity.
Smartphone forensics is a dynamic and ever-evolving discipline since forensic practitioners’ techniques change along with the technology they use. Understanding the types of digital forensics and the specifics of mobile devices forensics allows professionals to handle a wide range of challenges associated with modern smartphones.


 1. MOBILedit Forensic
1. MOBILedit Forensic