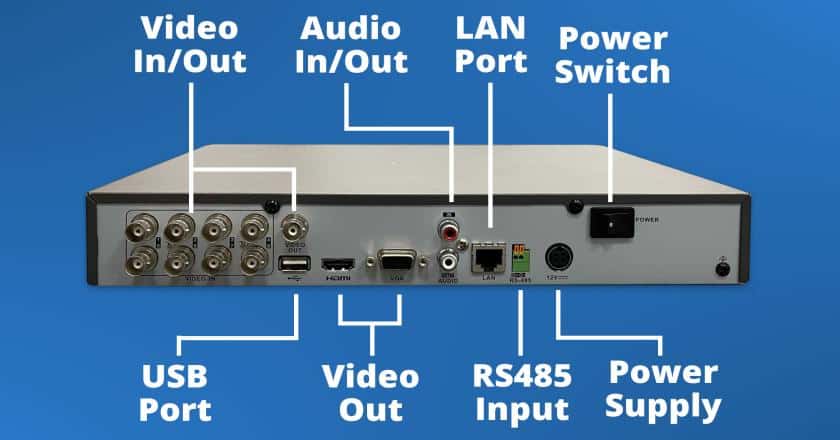
Digital video recorder (DVR) technology has revolutionized the world of video surveillance. Unlike traditional videotape systems, DVR recorders have the capacity to transform analog signals from video cameras into digital format. After conversion, the converted video data is saved on a hard drive, where it is easy to find, quick to use, and helpful for organizing recordings. Since DVR technology has substantially improved the usability and dependability of surveillance systems, it is a crucial part of today’s security architecture.
What is DVR and How DVR Recorders Work in Video Forensics?

-
Content
- Overview of DVR Recorders
- Importance of Video Forensics
- How DVR Recorders Work in Video Forensics?
- Future Trends of DVRs in Video Forensics
- Conclusion
-
Content
- Overview of DVR Recorders
- Importance of Video Forensics
- How DVR Recorders Work in Video Forensics?
- Future Trends of DVRs in Video Forensics
- Conclusion
Overview of DVR Recorders
1. Features and Functionalities of a DVR
First of all, what is DVR? DVR is a sophisticated computer device that used to record video from security cameras and store it on a hard disk. DVR recorders are superior to earlier video technologies because of their enormous store capacity and the ease of digital searching and playback.
The DVR meaning extends to its role as the cornerstone of a DVR security system, which has a wide range of features and capacities that make them more valuable than basic recording devices. These include the ability to view live or previously recorded video from any location using the internet, as well as high-definition video quality, real-time recording, and remote access features. Additionally, some DVR recorders have cutting-edge features like motion detection, facial recognition, and automatic warnings, increasing their usefulness in a variety of security and surveillance applications. DVR systems are made even more potent by integration with DVR forensics software, which helps with video forensics and SVR activities.
2. How DVRs Capture and Store Video Data
The way DVRs capture and store video data is an essential aspect of their operation. DVRs connect directly to surveillance cameras, continuously receiving analog video signals. When connected to analog cameras, DVRs can directly receive and process analog video signals. The analog-to-digital conversion and encoding functions are performed by the DVR itself. The recorded video is then stored on a built-in hard drive or external storage connected to the DVR. This stored data, or video evidence, can later be retrieved and analyzed for various purposes, including security monitoring and forensic investigations.
Importance of Video Forensics
1.Video Forensics and Its role in Analyzing and Investigating Recorded Video Footage
Technology and investigative sciences are combined in the field of video forensics. It entails gathering, processing, and deciphering video evidence gathered from a variety of sources, including DVR recorders.
Analyzing and looking into recorded video footage requires the use of video forensics, which is crucial. It includes the study and use of a wide variety of techniques, such as the restoration of deleted or damaged video data, the improvement of video quality, and the detection of anomalies. Experts in video forensics do these operations quickly and accurately by using state-of-the-art technologies. The objectivity of video forensics is important. Digital video records provide an unbiased view of what transpired, and with careful investigation, forensic experts may piece together an accurate narrative. This scientific method of video evidence analysis and decoding provides a substantial advantage in court investigations by identifying wrongdoers, exonerating the guilty, and providing clarity in ambiguous situations. In order to discover the truth from video recordings and maintain justice and fairness in our society, video forensics is therefore crucial.
2. Examples of Scenarios Where Video Forensics is Crucial
The use of video forensics in various situations is widespread and crucial, and it has made significant contributions to solving challenging problems in various fields.
For law enforcement, video forensics is an invaluable ally, in which it can be used to identify criminals or establish the innocence of suspects in a variety of crimes, including violent ones and theft cases. By using DVR forensics software, law enforcement organizations are better able to glean useful information from unprocessed video footage.
Video forensics is also crucial for security operations. The major investigative tool in any case of trespassing, industrial espionage, or unlawful entry is the forensic study of security footage. In situations like these, tools like SalvationDATA’s VIP 2.0 is crucial for correcting video file errors and guaranteeing thorough Surveillance Video Recovery.
Video forensics also provides vital evidence in accident investigations to pinpoint fault and accountability. Accident reconstructions using video footage from dash cams, traffic surveillance cameras, or DVR recorders can definitively demonstrate the series of events leading up to the accident. Video forensics tools and other open source digital forensic tools work together to produce conclusive evidence by ensuring a more accurate and thorough investigation.
Video forensics continues to be a key element in all of these circumstances, providing justice, preserving security, and protecting accountability in our society.
How DVR Recorders Work in Video Forensics?
DVRs are crucial in video forensics in addition to monitoring. Through the use of a video forensic tool, investigators frequently use DVR recordings to solve crimes and resolve disputes and they can work on video forensics from these aspects:
1. Continuous Video Recording
DVR recorders are typically set up to continuously record video footage from connected surveillance cameras. This continuous recording ensures that no critical moments are missed, and a comprehensive record of events is maintained.
2. Storage and Compression
The recorded video data is stored on the DVR’s internal storage or external hard drives. To optimize storage space, DVRs often use video compression techniques, such as H.264 or H.265, to reduce the size of the video files without significant loss of quality.
3. Timestamp and Metadata
Modern DVR recorders also add timestamps to the video frames, providing accurate information about when each frame was captured. Additionally, metadata, such as camera location, settings, and other relevant details, may be embedded to aid in the investigation process.
4. Event Triggering
Some advanced DVR recorders support event triggering, where specific events, such as motion detection or sensor alerts, can prompt the DVR to record additional frames before and after the triggered event. This feature helps capture crucial moments leading up to an incident.
5. Authentication and Integrity
To ensure the authenticity and integrity of the recorded footage, DVRs employ digital signatures or hash functions to verify that the video data has not been tampered with after its recording.
6. Forensic Software Integration
In video forensics, specialized software tools, like the DVR forensics software mentioned earlier, can be used to extract evidence from DVRs more efficiently. These software packages offer advanced features like intelligent video retrieval, keyword searches, and analysis of multiple video streams to aid investigators in uncovering crucial evidence.
7. Chain of Custody
Maintaining the chain of custody is crucial in video forensics. The DVR recorder’s logs, along with the forensic software’s generated reports, help document every step of the investigation and ensure that the video evidence remains admissible in court.
8. Expert Analysis
Despite the advanced capabilities of DVR recorders and forensic software, expert analysis by trained video forensic specialists is indispensable. These experts can enhance video quality, clarify details, and provide professional opinions based on their analysis.
Future Trends of DVRs in Video Forensics
1. Advancements in Video Forensics Research and Development
Due to ongoing improvements in research and development, the future of video forensics contains intriguing potential. The capabilities of forensic tools like VIP 2.0 by SalvationDATA will advance along with technology. Video evidence analysis will likely be further improved by advanced algorithms and machine learning, which will improve the accuracy and effectiveness of extracting important details from recorded film. A further benefit of improvements is that they may solve problems like managing encrypted video data or coping with new video formats, ensuring that video forensics remains a potent investigative tool.
Contact us to have a Free Trial now!
2. Integration of Video Forensics with Internet of Things (IoT)-based Devices
We may expect the integration of video forensics with Io T-based devices as the Internet of Things (Io T) grows in popularity. DVR recorders and surveillance cameras will develop more intelligence and connectivity. Real-time notifications prompted by specific circumstances and remote access and management of video recording will be made possible through integration with Io T devices. In order to build a more complete picture of the events under investigation, this synergy will further enable investigators to gather evidence from other sources, such as wearable cameras, drones, and home security systems.
3. Real-time Processing and Analysis of DVR Footage
Real-time processing and video analysis hold the key to the future of DVRs and video forensics. DVR systems will be able to analyze video data instantly as processing power rises and algorithms become more effective. This entails instant warning in response to predetermined triggers, automatic event tagging, and immediate recognition of questionable actions. By combining machine learning, real-time video analytics will become more robust, decreasing the need for post-event analysis and allowing for quick response to avoid incidents or address ongoing situations.
Conclusion
DVR recorders play a pivotal role in video forensics by capturing, storing, and preserving crucial video evidence. When combined with specialized forensic software and the expertise of trained investigators, DVRs become powerful tools in uncovering the truth behind complex legal matters.Specialists may extract critical information from unprocessed video with the use of cutting-edge forensic tools like VIP 2.0 by SalvationDATA and its high-resolution recordings, assisting in the investigation of crimes, resolving legal disputes, and maintaining the rule of law.