In the digital universe, where data reigns supreme, maintaining the integrity of file extraction is non – negotiable. MD5 and SHA checksums stand as two stalwart guardians in this domain. MD5, with its long – standing presence, offers speed and compatibility. SHA brings enhanced security. Together, they form a powerful duo, ensuring that files remain pristine during extraction, free from corruption and tampering.
Ensuring File Extraction Integrity with SHA and MD5 Checksum

-
Content
- MD5 And SHA
- Security Profile: SHA v.s. MD5
- Why Use Both MD5 And SHA?
- How MD5 and SHA Drive Security in Salvationdata Products
-
Content
- MD5 And SHA
- Security Profile: SHA v.s. MD5
- Why Use Both MD5 And SHA?
- How MD5 and SHA Drive Security in Salvationdata Products
MD5 And SHA
In the digital age, data is crucial, and file extraction integrity is particularly vital in e – forensics and file backup. In e – forensics, even a minor file alteration can derail an investigation, potentially leading to miscarriages of justice. For file backup, corrupted files during extraction render backups useless, resulting in significant losses when disasters or cyber – attacks strike.
To tackle these issues, MD5 and SHA have become mainstream hash function algorithms. MD5 is known for speed and calculation simplicity, while SHA comes in various types like SHA – 1, SHA – 2, and SHA – 3, each with different security and performance levels. The following sections will explore their workings, pros and cons, and applications.
Understanding of the MD5 and SHA checksum
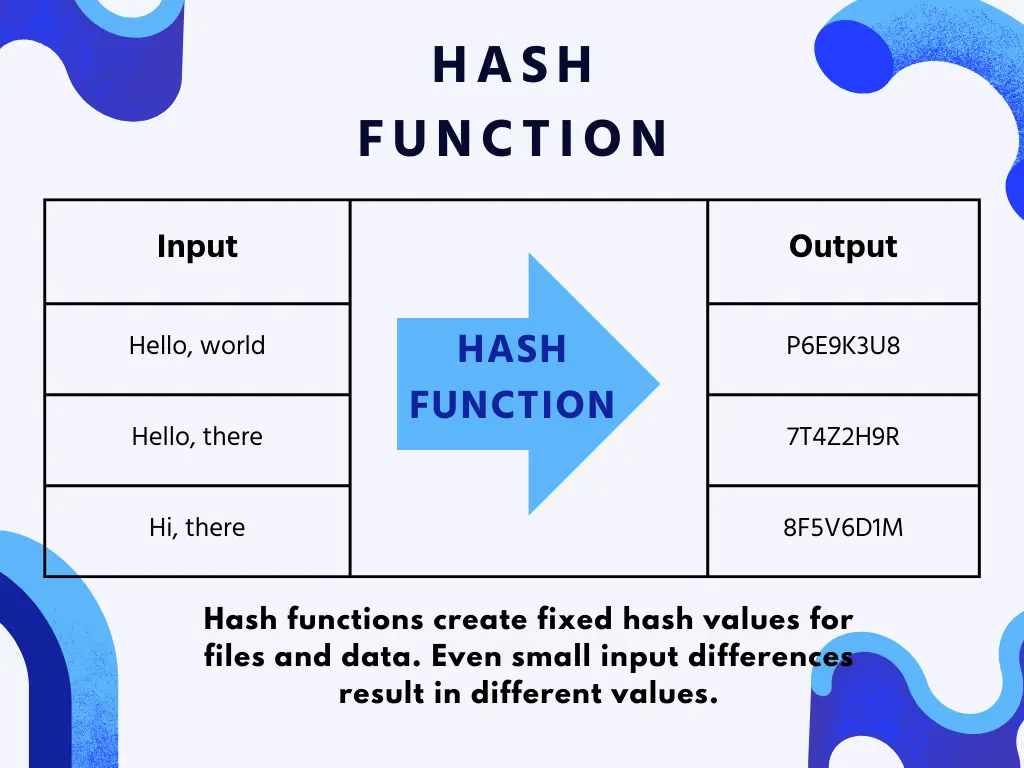
MD5 and SHA are just different types of hash functions. They rely on the features of hash functions to keep data in check and boost security. You may ask, “What is a hash function?” So now, let’s begin by figuring out what exactly a hash function is.
What is a hash function?
The hash function is the function that maps data of any size to fixed – size hash values. It has the avalanche effect (small input change leads to large hash change).
What is MD5?
MD5 message-digest algorithm is a has function which is widely used for producing a 128-bit hash value. It is designed Ronald Rivest in 1991 to replace earlier MD4. It generates 128-bit hash value for ensuring file integrity.
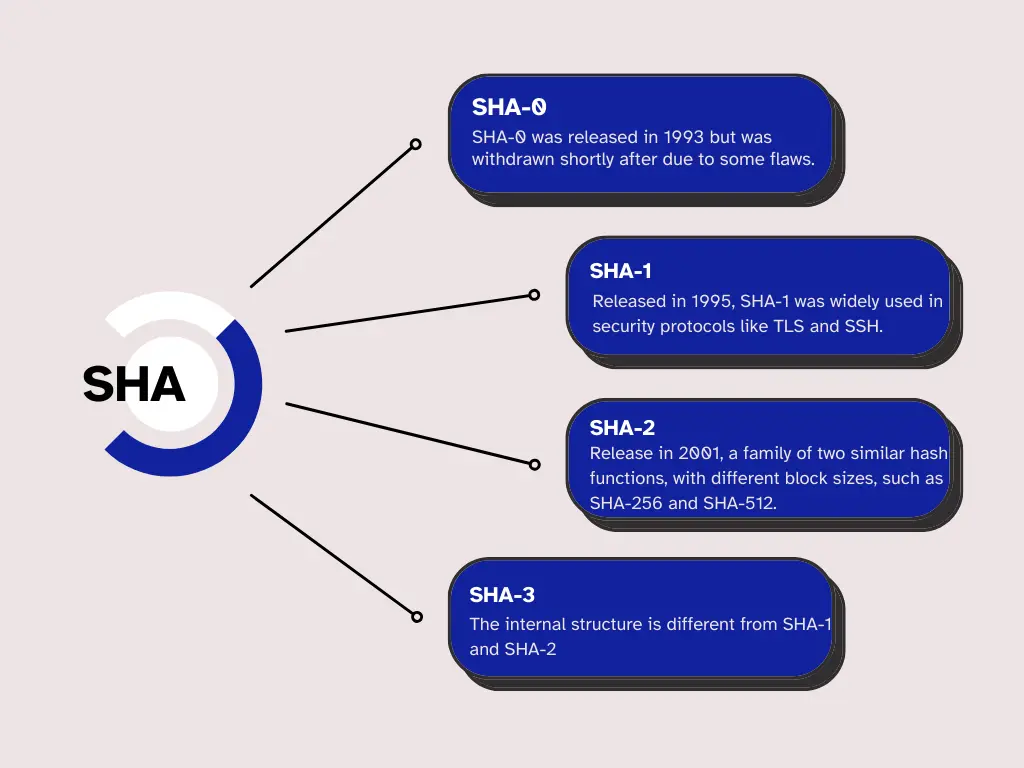
What is SHA?
The Secure Hash Algorithms, published by NIST, are a series of cryptographic hash functions includes SHA-0 (published in 1993), SHA – 1 (published in 1995), SHA – 2 (published in 2001), and SHA – 3 (published in 2015).
Security Profile: SHA v.s. MD5
Is MD5 secure?
In 2004, the MD5 is shown that it is not collision-resistant. This collision vulnerability results in the same hash value being generated for two different inputs. However, MD5 still has its own little corner. In situations where security isn’t a major concern, such as when home users are just doing basic checks to see if their backup files are okay, or when there’s hardly any chance of a collision attack happening, MD5 can still come in handy. After all, it’s simple to use and really fast.
Is SHA secure?
SHA is far more secure. SHA – 1 has issues and is being phased out. SHA – 2, with its long – length hashes, is a security staple, as seen in Bitcoin and SSL/TLS. SHA – 3, developed against future threats like quantum attacks, offers similar security and is gaining ground in high – security fields.
Why Use Both MD5 And SHA?
Balancing Speed and Security
- MD5: MD5 is really quick when it comes to calculating hash values. In situations where there’s not much risk, like when home users are backing up their files and the chances of security threats are super low, MD5 can rapidly check if the files are okay. Also, for those older systems that don’t have a lot of resources, MD5’s speed is a huge plus. It helps keep these systems from getting overloaded.
- SHA: SHA, especially SHA – 256 and SHA – 512, offers a higher level of security. Their complex algorithms, built to resist attacks, make them slower. But the reduction in speed trades an increase in safety.
Compatibility and Redundancy
- MD5 ensures compatibility with legacy tools and workflows.
- SHA provides a powerful safeguard for critical file integrity checks, ensuring the authenticity of any data.
How MD5 and SHA Drive Security in Salvationdata Products
-
AFA9500: Leveraging MD5 for Swift Data Integrity Verification
The new generation of mobile forensic devices AFA9500 uses MD5 checksums to verify data integrity. When the AFA9500 scans a mobile device, MD5 quickly captures various types of data (text messages, phone status, installed application content, and other content).
-
SPF Pro (SmartPhone Forensic Solution): MD5 checksum for File Integrity and Authentication
Like AFA9500, SPF also has MD5 checksum settings, which is essential for file extraction integrity verification.
-
DBF (Database Forensic Analysis System): Multiple file verification methods
DBF6300 uses multiple hash functions, including MD5, SHA1, SHA256, and SHA512, which enables DBF6300 to achieve a better balance between speed and security.