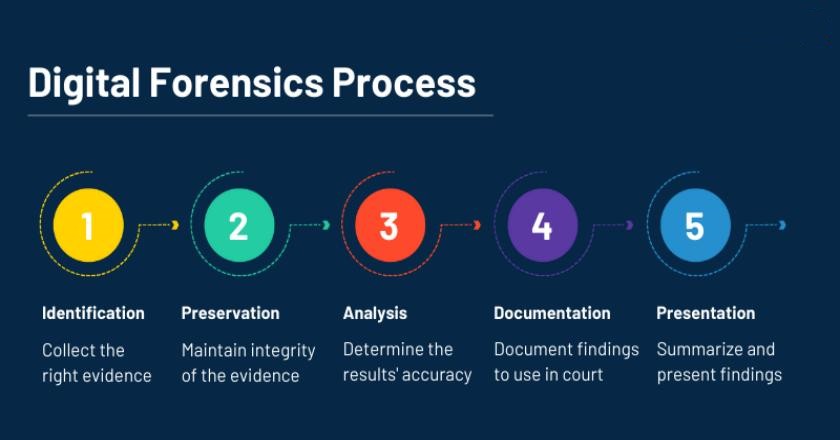
Digital forensics is an important part of defense that focuses on finding and understanding computer data. The process is usually legal and is mostly used to get back and look into information found on digital devices, usually in connection with computer crimes. Digital forensics is very important because it helps solve crimes by finding proof and following the digital footprints that criminals leave behind.
Professionals in the field need to know how the digital forensics process works because it has many specific steps, such as finding possible sources of digital evidence and then collecting, studying, and showing this information in court in the right way. Each step is very important and needs close attention to detail to keep the evidence’s purity and make sure it can be used in court. This review sets the stage for a more in-depth look at each important step of the digital forensics process. It also shows how important digital forensics is in modern forensic science and hacking.